
Onsite and Offsite Benefits of Sustainable Land Management
The Onsite and Offsite Benefits of Sustainable Land Management (SLM) project raises awareness and addresses the benefits of action and costs of inaction in areas where SLM practices are implemented (onsite), and the impacted areas downstream (offsite).
- Home
- Onsite and Offsite Benefits of Sustainable Land Management
About the project
The Sustainable Development Goals have emphasized that SLM is at the core of global environmental and development issues. SLM simultaneously addresses food security, climate change adaptation and mitigation, disaster risk reduction, biodiversity, and water conflict resolution. However the value and importance of scaling-up SLM is not yet sufficiently acknowledged by policymakers or the broad public, thus hindering the allocation of adequate resources to combating land degradation.
Although information and data on land degradation and SLM are increasing worldwide, there is a lack of evidence and awareness on the specific impacts of SLM onsite and offsite. Evidence-based examples highlighted in each case study help to target these gaps by raising awareness and increasing knowledge about various interlinked impacts in areas onsite, where SLM is directly implemented (upstream), and offsite areas (downstream).
WOCAT (The World Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies) investigates both unsustainable and SLM in Columbia, Indian Himalayas, Haiti and Iceland; identifying, assessing, and illustrating the onsite and offsite impacts of different SLM practices. Onsite investigations focus on the effects on land degradation, water availability and quality, resilience of land and people and biodiversity. Offsite impacts (often neglected and underestimated) focus on downstream water availability and quality (for domestic use, irrigation and hydropower), deposition of particles from windstorms, as well as disaster risk reduction related to floods, droughts and sand and dust storms.
Approaches and technologies giving both onsite and offsite benefits are emphasized in the findings and further documented in detail (WOCAT SLM database). The case studies prompt policy action and public support for investments that improve livelihoods, ecosystem services and natural resource management. Recommendations are focused on SLM-based approaches that enhance collaboration at the local, national and international level.
The project was implemented by WOCAT jointly with various partner organizations, and financially supported by the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation.
Key Terms
Onsite: locations where land management practices are applied – implementation site of SLM
Offsite: areas where land management practices (applied elsewhere) have an impact on the surrounding land and people, including areas downstream (related to water) or downwind (related to wind transport of sand, dust and moisture)
Benefits of action: economic well-being, climate resilience, environmental impacts (cleaner air and water, enhanced preservation of land and natural resources), community building, equity
Costs of inaction: yield losses, land and resource degradation, increased disaster risk and vulnerability to climate change, poverty
In this project, case studies to demonstrate the on- and offsite impacts were developed in four countries. The results and their implications for practice, policy and research are presented in Policy Briefs , videos and the documentation of several SLM Technologies and SLM Approaches. Furthermore, a Watershed Tool was developed and applied to assess on- and offsite impacts.
--> Only few cases are presented to raise awareness. If you are interested to share further cases, please contact us and we will send you further information and the instructions on how to develop, present and upload them on this website.
Case Studies
The following case studies have been selected to present a range of different on- and offsite impacts in different countries and contexts such as land management to reduce flood disaster risks (Haiti) to improve the recharge of springs (India and Haiti), to reduce damaging behaviour of rivers in a large watershed (Colombia) and to protect farmland and towns from devastating sand and dust storms (Iceland). The selection was strongly guided by the interest of WOCAT partner countries. Additional examples have been identified about phosphorous contamination and dying up of lakes in Switzerland and drinking water supplies for cities like Nairobi and hydropower generation in Kenya. Some results are presented will be presented to be further elaborated in follow-up projects.
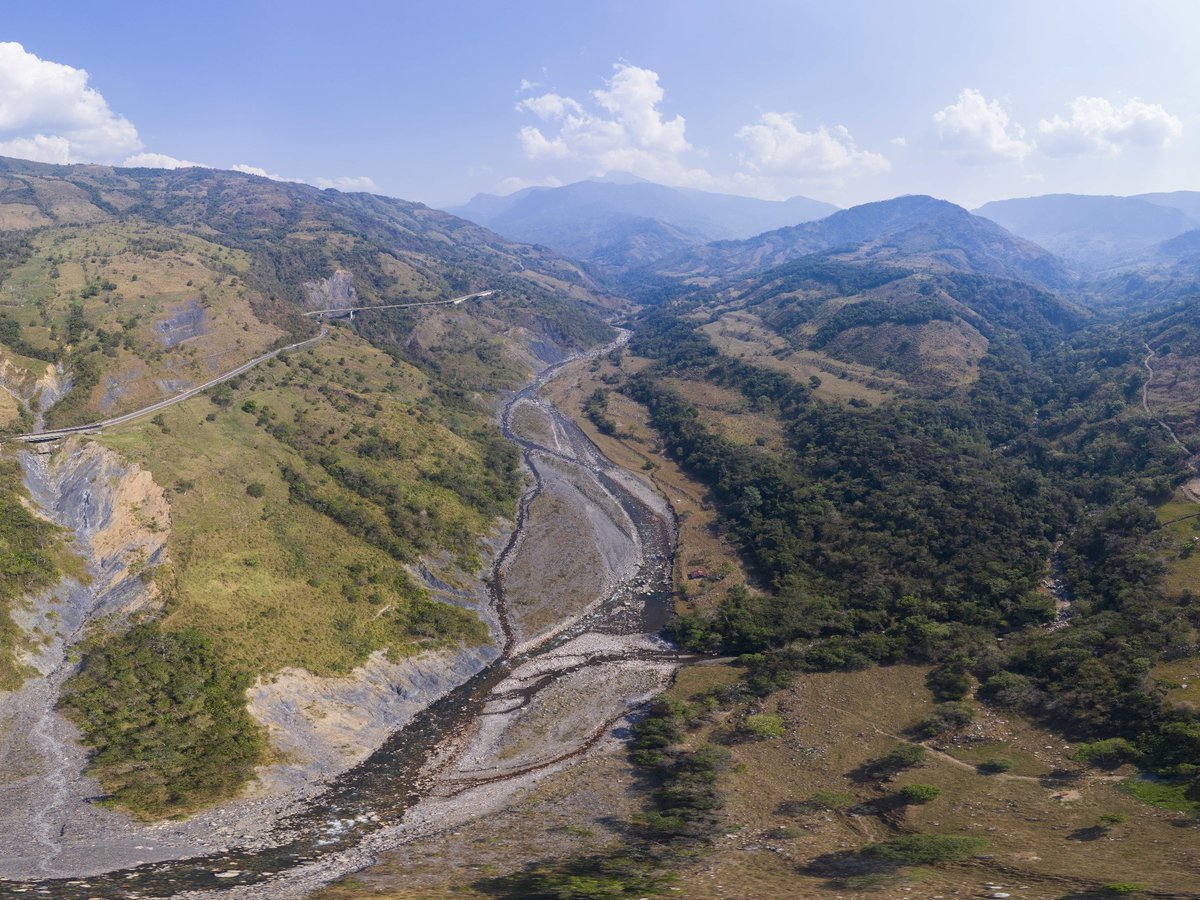

In large watersheds such as the Cusiana watershed, there are complex and diverse onsite and cumulative offsite impacts of land management in each ecosystem (ranging from Andean Páramo at 4000 m, to the cloud forests at 2000 m, to savannah lowlands at 200 m).
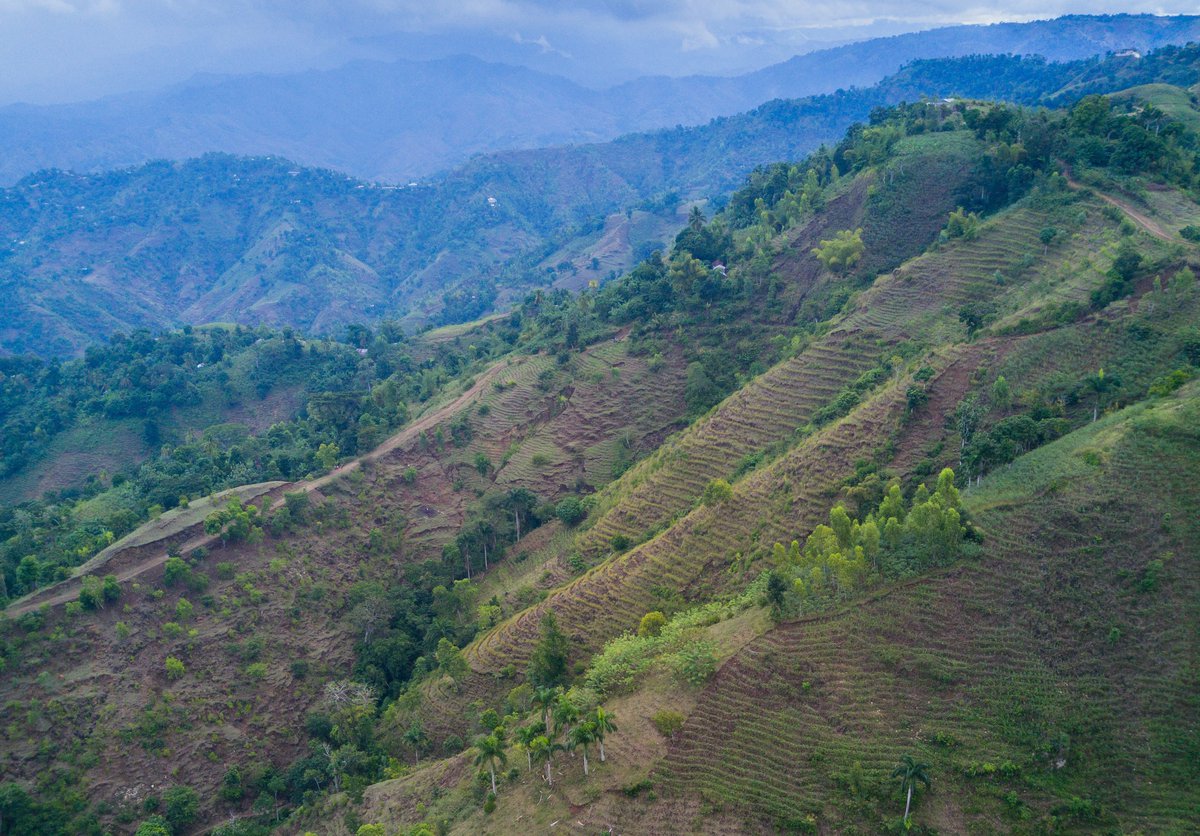

In Haiti, SLM practices (eg. agroforestry and vetiver grass terraces) can enhance the resilience of land, and people, to tropical storms, floods and droughts.

Springs, the “blue life-points” of Himalayan mountain populations, are recharged through springshed protection, community forest management, conservation of broadleaf forests and recharge structures.
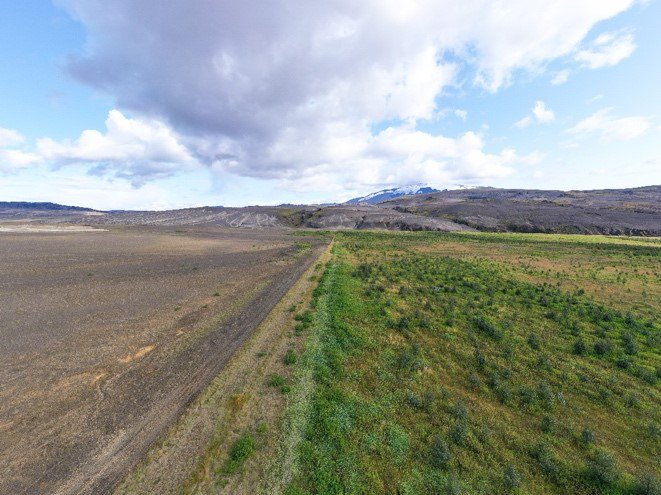

Revegetation measures with lyme grass, birch trees and lupine, combined with grazing management in Iceland’s volcanic highlands and coastal communities mitigates soil losses and reduces wind erosion.
On- and Offsite Products

Illustrated Policy Briefs present for each case study the main impacts of SLM both on- and offsite with facts, figures and latest insights. They show key messages, and the implications for practice, policy and research.
They guide decision making in implementation and provide evidence that SLM is not only for the benefits of a few land users but for all, rural and urban people. This raises the awareness about the overall value SLM and the willingness to invest in good land management. The attractive 6 pages layout offers key insights and recommendations for project implementers, planners, policy makers and researchers it also shows links to videos and references for further reading.
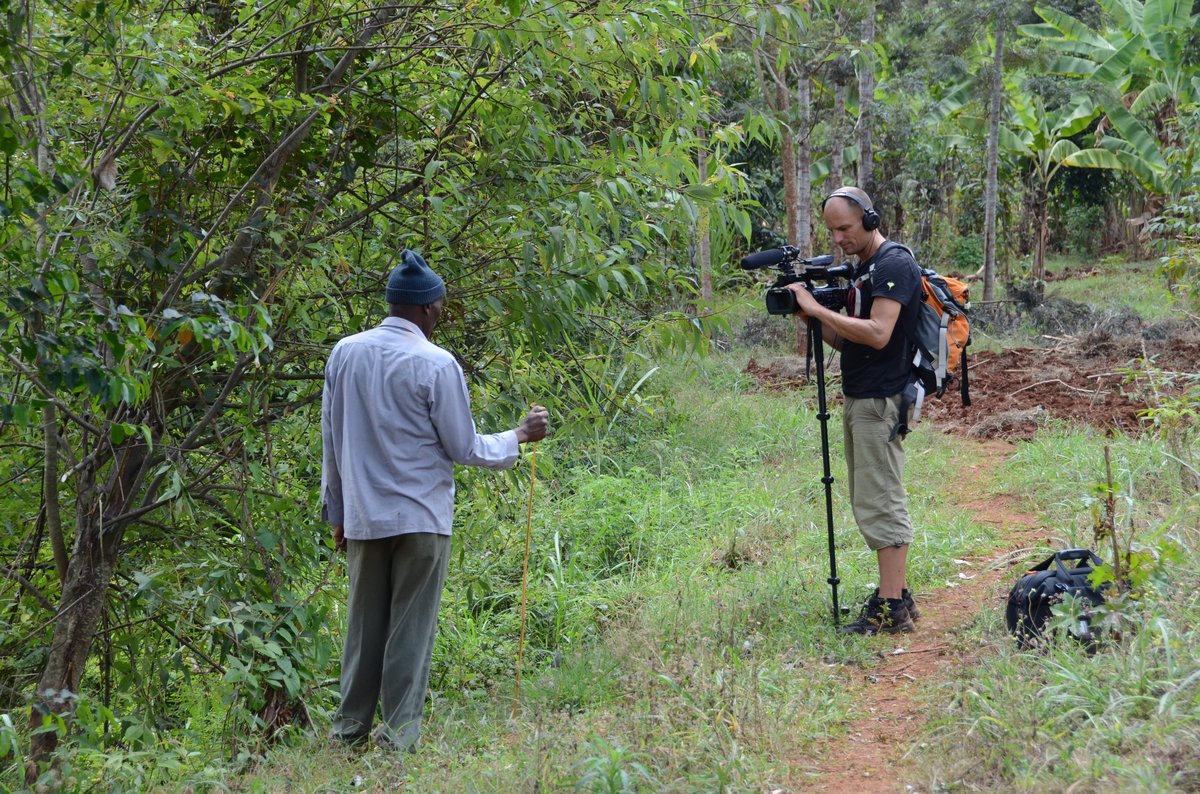

For different case studies attractive videos illustrating the insights of both on and off-site impacts of current and improved land management. The videos complement the Policy Briefs with impressive imagery and statements by land users and SLM specialists.
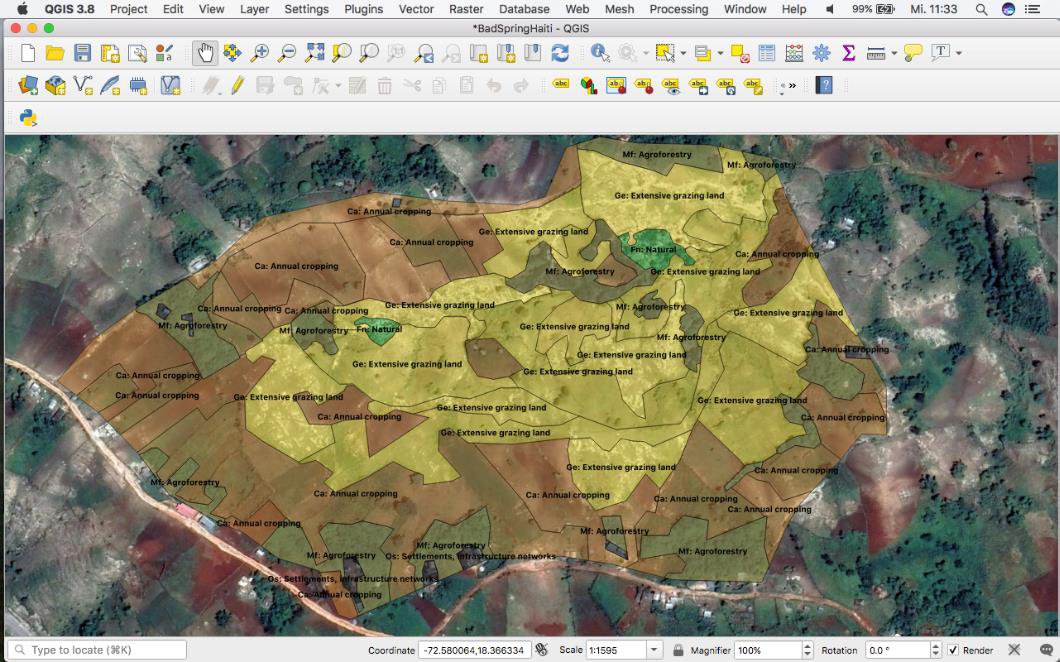
The Watershed Tool helps to categorize and map different land use/land management types, calculate their runoff rates, and determine their contribution to the total watershed runoff from daily rainfall events.
--> A prototype is available upon request wocat.cde@unibe.ch
Contact
 Switzerland
SwitzerlandProject duration
2016 - 2020
Video Teaser about the Project
Video for the Desertification and Drought Day 2020
Synthesis Report
The report presents results from cases of different on- and offsite impacts of both unsustainable and sustainable land management in Columbia, Indian Himalayas, Haiti and Iceland. It highlights the importance of an overall assessment of SLM impacts and the implications for practice, policy and research.
--> Available soon!






